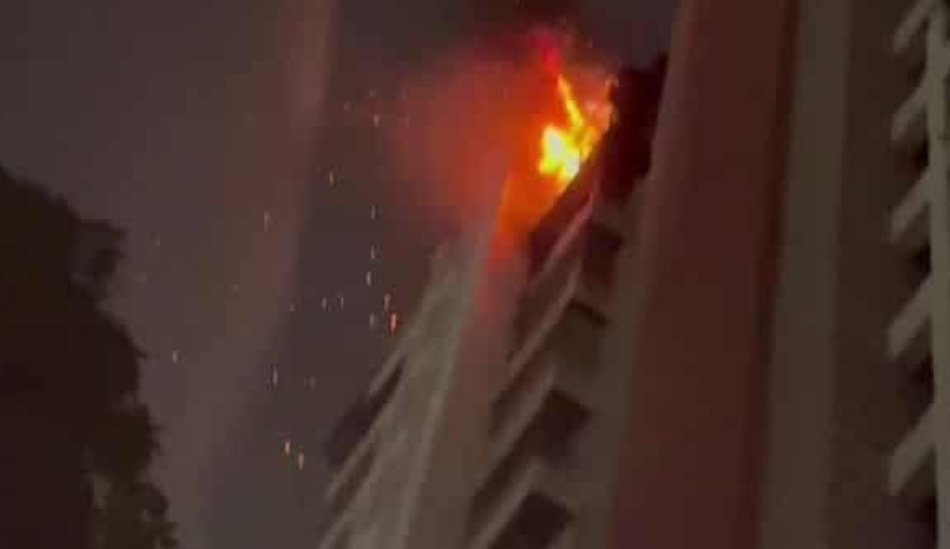
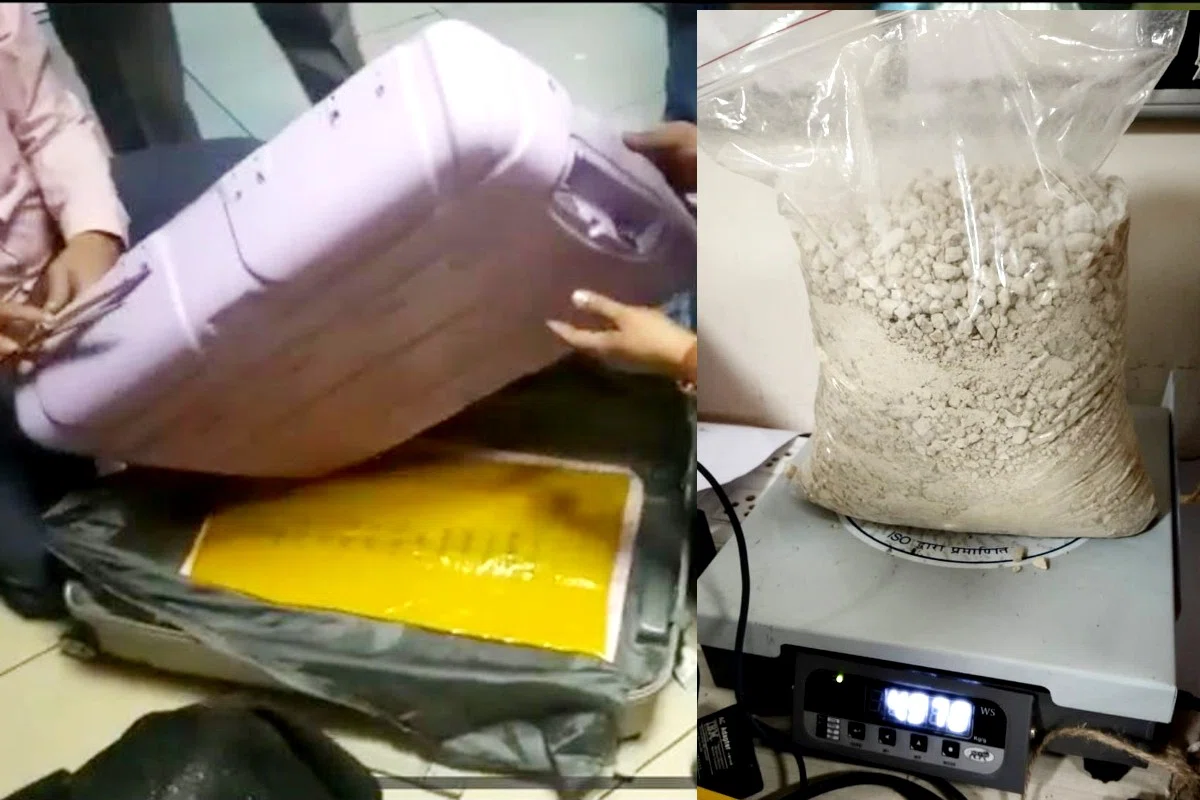
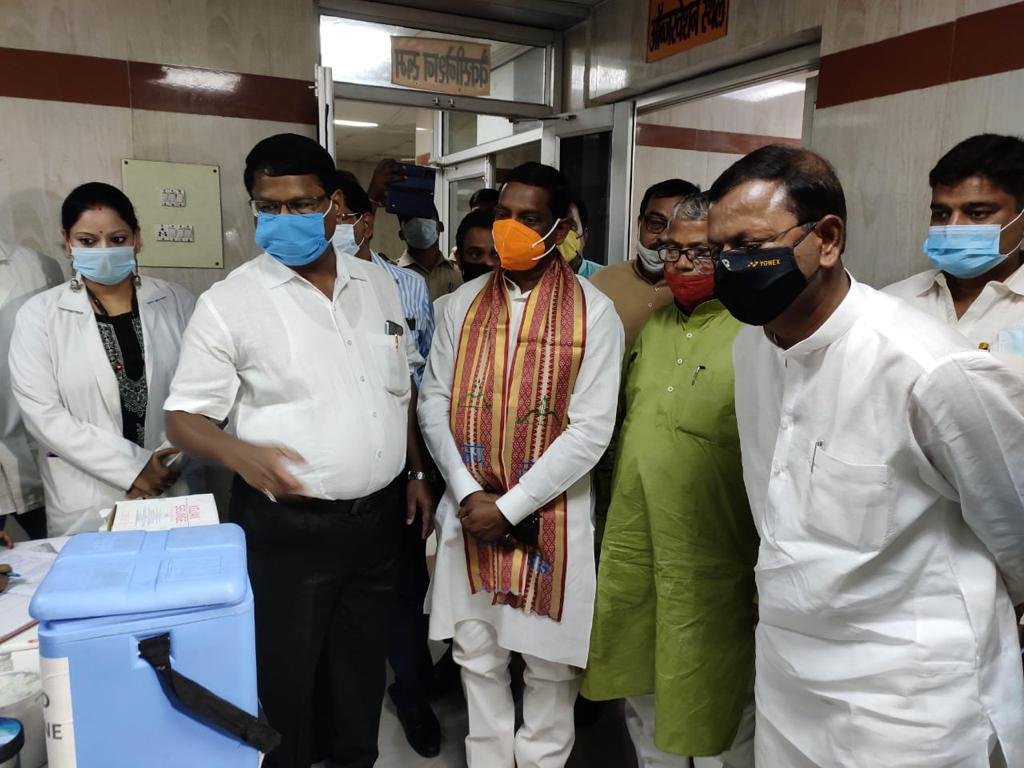
CONAKRY, Aug 9 – Health experts in Guinea have affirmed one passing from Marburg infection, an exceptionally irresistible hemorrhagic fever like Ebola, the World Health Organization said on Monday.
It denotes the first occasion when that the destructive sickness has been distinguished in West Africa. There have been 12 significant Marburg episodes since 1967, for the most part in southern and eastern Africa.
Guinea’s new case was first distinguished last week, only two months after the nation was pronounced liberated from Ebola following a concise erupt recently that killed 12 individuals.
The patient, who has since capitulated to the disease, first looked for treatment at a neighborhood facility before his condition quickly weakened, the WHO explanation said.
Experts at Guinea’s public haemorrhagic fever research center and the Institute Pasteur in Senegal later affirmed the Marburg conclusion.
“The potential for the Marburg infection to spread all over implies we need to leave it speechless,” Matshidiso Moeti, WHO’s Regional Director for Africa, said in the articulation.
“We are working with the wellbeing specialists to execute a quick reaction that expands on Guinea’s past experience and mastery in overseeing Ebola, which is sent along these lines,” Moeti said.
Both the Marburg case and the current year’s Ebola cases were recognized in Guinea’s Gueckedou region, close to the lines with Liberia and Ivory Coast. The primary instances of the 2014-2016 Ebola pandemic, the biggest ever, additionally were from a similar locale in Southeastern Guinea’s timberland district.
Marburg case casualty rates have differed from 24% to 88% in past flare-ups relying upon infection strain and case the executives, WHO said, adding that transmission happens through contact with tainted body liquids and tissue. Indications incorporate migraine, spewing blood, muscle torments and seeping through different holes.